
Asia-Pacific Genetic Testing Market Analysis by Mordor Intelligence
The Asia-Pacific genetic testing market is expected to grow from USD 1.82 billion in 2025 to USD 1.98 billion in 2026 and is forecast to reach USD 3.01 billion by 2031 at 8.78% CAGR over 2026-2031. Continuous government investment in national genomics programs, declining sequencing costs that now hover near USD 500 per whole genome, and the rapid clinical acceptance of comprehensive genomic profiling in oncology anchor demand fundamentals. Mid-size laboratories are scaling NGS workflows to keep pace with hospital requirements, while tele-genetics platforms broaden access in rural segments that had previously been excluded from advanced diagnostics. Regulatory fragmentation remains the chief obstacle, yet that same complexity creates high switching costs that protect country-specific incumbents. The convergence of artificial intelligence–assisted variant interpretation with maturing reimbursement policies signals an approaching tipping point when precision testing becomes a mainstream clinical service rather than a specialized referral procedure.
Key Report Takeaways
- By technology, Next-Generation Sequencing held 37.84% of Asia-Pacific genetic testing market share in 2025, while CRISPR-based enrichment is projected to register the fastest 8.89% CAGR to 2031.
- By application, cancer diagnosis and prognosis captured 33.34% of Asia-Pacific genetic testing market size in 2025, yet rare disease diagnostics is advancing at a 9.18% CAGR across the forecast horizon.
- By end user, hospitals and clinics accounted for 40.65% of Asia-Pacific genetic testing market share in 2025, whereas tele-genetics service providers are poised for a 9.47% CAGR through 2031.
- By geography, China commanded 47.78% of Asia-Pacific genetic testing market share in 2025, whereas India is set to expand at a 9.72% CAGR through 2031.
Note: Market size and forecast figures in this report are generated using Mordor Intelligence’s proprietary estimation framework, updated with the latest available data and insights as of January 2026.
Asia-Pacific Genetic Testing Market Trends and Insights
Driver Impact Analysis
| Driver | (~) % Impact on CAGR Forecast | Geographic Relevance | Impact Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|
| Expanding NGS-based oncology & rare-disease diagnostics | +2.8% | Global, with concentration in China, Japan, South Korea | Medium term (2-4 years) |
| National genomics initiatives (China, India, Japan) | +2.1% | China, India, Japan, with spillover to ASEAN | Long term (≥ 4 years) |
| Declining sequencing costs | +1.9% | Global | Short term (≤ 2 years) |
| Tele-genetics adoption in emerging APAC | +1.4% | India, Southeast Asia, rural China | Medium term (2-4 years) |
| CRO-led precision-oncology trial demand | +0.8% | Regional hubs: Singapore, Hong Kong, Australia | Medium term (2-4 years) |
| Source: Mordor Intelligence | |||
Expanding NGS-based Oncology & Rare-Disease Diagnostics
Liquid biopsy platforms validated in trials such as the CIRCULATE-Japan GALAXY study have shifted postoperative colorectal cancer surveillance toward circulating tumor DNA testing that predicted recurrence risk with 12-fold higher accuracy than conventional markers. National insurance in Japan now reimburses comprehensive genomic profiling, prompting neighboring regulators to re-evaluate coverage criteria. The SCRUM-Japan GOZILA project further demonstrated that liquid biopsy–guided therapies doubled median overall survival, reinforcing the clinical and economic rationale for routine genomic assays. Rare-disease programs leverage falling whole-genome prices to integrate sequencing into newborn screening agendas, especially as variant-interpretation AI tools compensate for shortages of trained genetic counselors in India and Southeast Asia. Together these shifts enlarge testing volumes and catalyze laboratory investments across primary care networks.
National Genomics Initiatives (China, India, Japan)
Government programs continue to build sovereign data assets and domestic laboratory capabilities that insulate local ecosystems from export controls and supply-chain shocks. India’s Genome India Project, having sequenced 10,000 representative genomes, supplies reference alleles that improve diagnostic accuracy for South Asian populations. In China, BGI Genomics is scaling colorectal cancer screening to roughly 800,000 individuals in Harbin, demonstrating industrial capacity for population-wide interventions. Japan’s nationwide whole-genome sequencing for cancer patients integrates clinical data with reimbursement, generating a feedback loop that propels adoption. These coordinated initiatives set common data standards, accelerate clinician education, and stimulate private investment in advanced sequencing hardware.
Declining Sequencing Costs
The cost curve for whole-genome sequencing dropped to nearly USD 500 per sample in 2024, rewriting economic thresholds for preventive programs. Vietnamese firm Gene Solutions processed more than 1.5 million direct-to-consumer kits in part because merged reagent purchasing across Southeast Asia magnifies scale economies. In Japan, GeneLife surpassed 2 million cumulative analyses by leveraging standard Illumina workflows backed with domestic logistics, reinforcing consumer trust. Laboratories that reach high throughput can negotiate bulk reagent discounts that undercut smaller peers, reinforcing market consolidation. Falling input prices also enable multiplex testing panels that bundle pharmacogenomics, cancer risk, and carrier status in a single workflow, improving revenue per sample without raising patient out-of-pocket costs.
Tele-genetics Adoption in Emerging APAC
Singapore’s familial hypercholesterolemia cascade screening program integrates telemedicine counseling with subsidized testing that covers up to 70% of patient fees, offering a blueprint for digitally mediated genomic services. Vietnam’s Genetica has developed proprietary gene-decoding chips tuned for Asian alleles and pairs them with AI risk calculators delivered through smartphone apps, circumventing brick-and-mortar counseling bottlenecks. Regulatory clarity around remote consent and data transfer in markets such as Australia fosters rapid scaling, while less mature frameworks in Indonesia slow cross-border tele-genetics offerings. As reimbursement shifts toward outcome-based models, digital providers that embed longitudinal monitoring gain competitive advantage.
Restraint Impact Analysis
| Restraint | (~) % Impact on CAGR Forecast | Geographic Relevance | Impact Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fragmented APAC regulatory frameworks | -1.8% | Regional, particularly affecting cross-border services | Long term (≥ 4 years) |
| Data-privacy & public-trust concerns | -1.2% | Global, with heightened sensitivity in developed APAC markets | Medium term (2-4 years) |
| Limited Asian reference genomes | -0.9% | China, India, Southeast Asia, with spillover to research applications | Long term (≥ 4 years) |
| Source: Mordor Intelligence | |||
Fragmented APAC Regulatory Frameworks
Divergent approval pathways require duplicate validation even for platforms with FDA or CE clearances, extending launch timelines by up to 18 months in Japan and 12 months in South Korea. Australia mandates separate laboratory accreditation under TGA guidelines that differ from Singapore’s Health Products Regulation Group, raising compliance costs for multinational laboratories. Smaller providers struggle to finance multiple dossiers, leading to country-specific monopolies that inflate test prices. Although ASEAN ministers discuss regulatory harmonization, tangible progress remains limited, prolonging market fragmentation through 2030.
Data-Privacy & Public-Trust Concerns
The 2023 breach that exposed genetic information of 7 million direct-to-consumer customers intensified calls for stricter oversight, culminating in a USD 30 million settlement and new disclosure obligations. Cultural sensitivities in Korea and Japan heighten anxiety about genetic discrimination, leading to cautious enrollment in population genomics initiatives. Australia enforces the Privacy Act Amendment 2024, which imposes heavier fines for unauthorized data transfers, prompting cloud vendors to localize infrastructure. Trust deficits particularly hinder direct-to-consumer and tele-genetics models where patient consent occurs online, limiting sample inflows until robust safeguards reassure users.
Segment Analysis
By Technology: NGS Platforms Drive Clinical Adoption
Next-Generation Sequencing held 37.84% of Asia-Pacific genetic testing market share in 2025 and remains the backbone for clinical oncology, while CRISPR-based enrichment is poised to grow at 8.89% CAGR through 2031 as laboratories emphasize targeted detection for liquid biopsy panels. The Asia-Pacific genetic testing market size for long-read sequencing is expanding as Genex introduced consumer PacBio Revio services priced at JPY 498,000 (USD 3,320) in 2025, demonstrating demand for structural-variant discovery beyond single nucleotide changes. Polymerase Chain Reaction retains relevance for point-of-care pathogen assays, especially in Southeast Asian clinics where instrument uptime and electricity remain constraints. Microarray platforms continue in ancestry and wellness testing, though clinical reimbursement shifts investment toward higher-resolution methods.
Laboratories are integrating artificial intelligence pipelines from firms such as GrandOmics to shorten variant-annotation cycles, improving report turnaround times from 10 days to 48 hours. Fluorescence in situ hybridization persists as a confirmatory step for chromosomal translocations in hematologic malignancies, mandated by Japanese oncology guidelines. Sanger sequencing maintains a niche for low-throughput single-gene confirmations in inherited cardiomyopathy panels, particularly when clinicians seek orthogonal validation. Collectively, the technology mix illustrates a strategic layering: comprehensive NGS for discovery, enrichment for surveillance, and legacy modalities for regulatory-driven confirmations, each reinforcing the Asia-Pacific genetic testing market as a multidimensional ecosystem.

Note: Segment shares of all individual segments available upon report purchase
By Application: Cancer Diagnostics Lead Clinical Adoption
Cancer diagnosis and prognosis captured 33.34% of Asia-Pacific genetic testing market size in 2025 on the strength of country-level reimbursement for comprehensive genomic profiling. Rare-disease diagnostics now records the fastest 9.18% CAGR as newborn screening programs in India and China adopt whole-genome panels that flag treatable metabolic disorders within 10 days of birth. Cardiovascular panels gain prominence through Singapore’s familial hypercholesterolemia initiative, which links genetic testing with subsidized statin therapy. Neurological applications lag due to limited therapeutic pathways, yet pharmacogenomic utility for seizure-management drugs stimulates pilot programs in Australia.
Consumer-led ancestry and wellness tests remain popular in Japan and South Korea, but the market is consolidating after several direct-to-consumer firms withdrew amid privacy litigation. The Asia-Pacific genetic testing market share for pharmacogenomics is set to expand as hospitals embed gene-drug interaction alerts into electronic medical records, reducing adverse events and hospital readmissions. Cancer liquid biopsy surveillance is shifting reimbursement from per-mutation billing to episode-of-care models, incentivizing multigene panels that track minimal residual disease. Collectively, evolving clinical evidence widens the application spectrum and anchors sustained growth across the region.
By End User: Healthcare Integration Accelerates
Hospitals and clinics accounted for 40.65% of Asia-Pacific genetic testing market share in 2025, reflecting direct integration into oncology and rare-disease care pathways. Diagnostic laboratories function as the operational core, running high-complexity assays and meeting ISO 15189 accreditation that many hospitals still lack. Tele-genetics providers are expected to record 9.47% CAGR through 2031, fueled by digital counseling platforms that bridge the specialist shortage in India’s tier-2 cities.
Academic centers remain vanguards for innovation, piloting single-cell sequencing and spatial transcriptomics under Japan’s Advanced Genome Support Program grants. Direct-to-consumer companies face stiffer oversight after data breaches prompted heightened consent standards, yet niche wellness offerings persist among health-conscious Millennials in urban China. Hybrid models emerge as providers pair online education with in-clinic sample collection, blending convenience with clinical legitimacy. This diversification of service channels embeds genetic testing deeper into routine care and expands total addressable volumes, thereby reinforcing the Asia-Pacific genetic testing market.

Note: Segment shares of all individual segments available upon report purchase
Geography Analysis
China maintained 47.78% share of Asia-Pacific genetic testing market in 2025, underpinned by sovereign sequencing capacity at BGI Genomics and population-scale colorectal screening that enrolled roughly 800,000 residents in Harbin. Domestic manufacturers dominate instrument sales after export-control uncertainties led hospitals to favor local supply chains. Strong provincial funding extends genetic services to county hospitals, although cross-province data transfer restrictions maintain data silos that limit nationwide clinical databases.
India is projected to grow at a 9.72% CAGR to 2031 as the Genome India Project standardizes reference genomes that improve variant calling accuracy for its diverse population. Public-private partnerships expand testing infrastructure in tier-2 cities, while mobile phlebotomy networks capture demand in rural districts. Declining reagent costs align with rising disposable incomes, propelling uptake of preventive panels that include cancer risk, pharmacogenomics, and carrier screening. Regulatory drafts that recognize tele-counseling certificates will further accelerate market penetration into underserved regions.
Japan represents a technologically mature node where comprehensive genomic profiling earns national insurance reimbursement, guaranteeing baseline volumes for cancer gene panels. The Japan Society of Clinical Oncology facilitates consensus on molecular residual disease guidelines, driving uniform adoption across tertiary centers. Meanwhile, Australia and South Korea leverage robust clinical-trial ecosystems that demand standardized NGS assays for biomarker-stratified enrollment, while Singapore pioneers subsidized genomic health programs embedded within its national primary care network. Rest-of-Asia-Pacific markets, including Malaysia and Vietnam, deploy genetic services within medical-tourism packages and AI-enabled risk assessments, though regulatory heterogeneity restricts multinational platform scalability.
Competitive Landscape
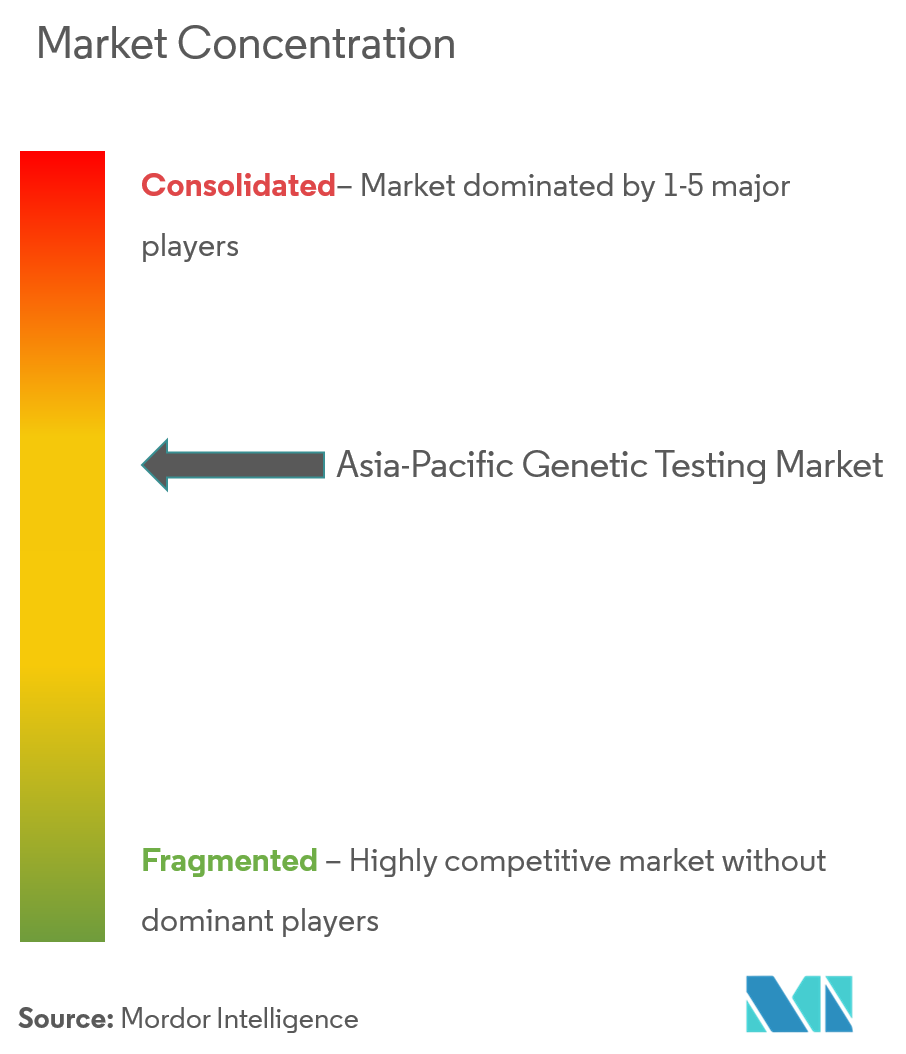
The Asia-Pacific genetic testing market features moderate concentration, leaving room for regionally specialized laboratories. BGI Genomics leverages an end-to-end offering of sequencers, reagents, and clinical services that anchors its leadership in China and supports expansion into Belt-and-Road partner countries. Illumina and Thermo Fisher continue to supply high-throughput instruments across the region, yet face localized competition from MGI and Oxford Nanopore, which negotiate bundled reagent contracts with provincial hospitals.
Platform convergence around NGS has reduced hardware differentiation, shifting rivalry toward turnaround time, bioinformatics quality, and regulatory depth. Tele-genetics newcomers exploit digital channels to win incremental volumes, often partnering with accredited labs for wet-lab processing while focusing on user acquisition and counseling interfaces. Strategic moves in 2024–2025 illustrate intensifying integration: Genex launched a consumer long-read WGS service, Takara Bio unveiled an automated single-cell system that processes 100,000 cells per run, and Regeneron acquired 23andMe to secure a proprietary biobank for drug-target discovery. Moderate entry barriers tied to accreditation and clinician relationships continue to check fragmentation, keeping the Asia-Pacific genetic testing market on a consolidation trajectory through 2030.
Asia-Pacific Genetic Testing Industry Leaders
Abbott Laboratories
Bio-Rad Laboratories Inc.
Myriad Genetics, Inc.
Genomic Health Inc.
Mapmygenome
- *Disclaimer: Major Players sorted in no particular order
Recent Industry Developments
- June 2025: Singapore's Ministry of Health announced plans for a national genetic testing program for Familial Hypercholesterolemia, offering means-tested subsidies up to 70% and cascade testing for family members through the Healthier SG clinic network
- October 2024: Macrogen was selected as preferred bidder for South Korea's "National Integrated Bio Big Data Project" worth KRW 606.5 billion, in consortium with DNA Link, Theragen Bio, and CG invites.
Asia-Pacific Genetic Testing Market Report Scope
A genetic test is a test performed to identify the presence of a particular gene or set of genes, with a particular sequence of the genome. The genes can be identified either directly through sequencing or indirectly through various methods. Genetic testing practices are rapidly increasing in rare disease diagnostics and for personalized medicines, which is driving the growth of this market.
The Asia Pacific Genetic Testing Market is Segmented by Type (Carrier Testing, Diagnostic Testing, Newborn Screening, Predictive and Presymptomatic Testing, Prenatal Testing, Other Types), Disease (Alzheimer's Disease, Cancer, Cystic Fibrosis, Sickle Cell Anemia, Thalassemia, Rare Diseases, Other Diseases), Technology (Cytogenetic Testing, Biochemical Testing, Molecular Testing), and Geography (China, Japan, India, Australia, South Korea and Rest of Asia-Pacific). The report offers the value (in USD million) for the above segments.
| Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) |
| Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) |
| Microarray |
| Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH) |
| Sanger Sequencing |
| Other Technologies |
| Cancer Diagnosis & Prognosis |
| Cardiovascular Disease Diagnosis |
| Neurological Disorder Diagnosis |
| Ancestry & Wellness |
| Other Applications |
| Hospitals & Clinics |
| Diagnostic Laboratories |
| Academic & Research Institutes |
| Direct-to-Consumer Companies |
| Other End Users |
| China |
| India |
| Japan |
| Australia |
| South Korea |
| Rest of Asia-Pacific |
| By Technology (Value) | Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) |
| Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) | |
| Microarray | |
| Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH) | |
| Sanger Sequencing | |
| Other Technologies | |
| By Application (Value) | Cancer Diagnosis & Prognosis |
| Cardiovascular Disease Diagnosis | |
| Neurological Disorder Diagnosis | |
| Ancestry & Wellness | |
| Other Applications | |
| By End User (Value) | Hospitals & Clinics |
| Diagnostic Laboratories | |
| Academic & Research Institutes | |
| Direct-to-Consumer Companies | |
| Other End Users | |
| By country | China |
| India | |
| Japan | |
| Australia | |
| South Korea | |
| Rest of Asia-Pacific |
Key Questions Answered in the Report
How big is the Asia-Pacific Genetic Testing Market?
The Asia-Pacific Genetic Testing Market size is expected to reach USD 1.98 billion in 2026 and grow at a CAGR of 8.78% to reach USD 3.01 billion by 2031.
What is the current Asia-Pacific Genetic Testing Market size?
In 2026, the Asia-Pacific Genetic Testing Market size is expected to reach USD 1.98 billion.
Who are the key players in Asia-Pacific Genetic Testing Market?
Abbott Laboratories, Bio-Rad Laboratories Inc., Myriad Genetics, Inc., Genomic Health Inc. and Mapmygenome are the major companies operating in the Asia-Pacific Genetic Testing Market.
What years does this Asia-Pacific Genetic Testing Market cover, and what was the market size in 2025?
In 2025, the Asia-Pacific Genetic Testing Market size was estimated at USD 1.98 billion. The report covers the Asia-Pacific Genetic Testing Market historical market size for years: 2019, 2020, 2021, 2022, 2023 and 2024. The report also forecasts the Asia-Pacific Genetic Testing Market size for years: 2026, 2027, 2028, 2029, 2030 and 2031.




